- Mon - Fri: 09.00am - 10.00pm
- 224A Khu Phố Hưng Thọ, Phường Hưng Định, TP Thuận An, Bình Dương
- suport@nguyenngoclog.com
What is CIF?
What is CIF? CIF price calculation formula?
CIF is one of the terms under Incoterms (International Commerce Terms) – set of international trade rules. The content of this set of rules revolves around the terms and regulations on the responsibilities of both buyers and sellers in foreign trade contracts.
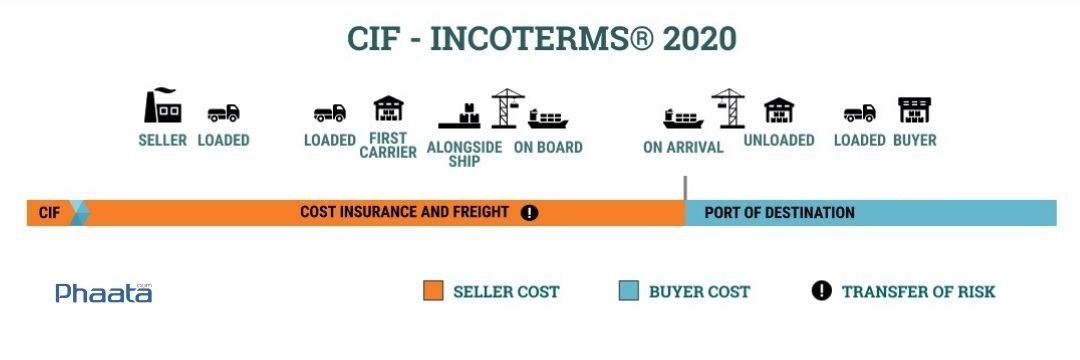
CIF stands for three factors: Cost, Insurance and Freight. All these factors combine to form the delivery conditions. This condition will often be written with the name of a certain seaport that performs the delivery and receipt function.
With CIF terms, the seller will be responsible for bringing the goods from the warehouse to the port, completing customs procedures, and at the same time bear all ship rental costs and cargo insurance fees until the goods arrive at the port. buyer.
The seller's responsibility actually ends when the goods are delivered to the sea carrier at the point of loading onto the ship. The buyer will receive the goods and complete customs procedures from the receiving port and bring the goods to the warehouse.
CIF price calculation formula: CIF price = FOB price + Sea freight + Cargo insurance fee
When a price is stated as CIF, this means that the seller's price includes the cost of the product, shipping costs as well as insurance of the goods up to the port of discharge.
What is the point of risk transfer in CIF?
The point of transfer of risk is the difference between the terms in Incoterms. In CIF, the point of risk transfer is at the port of departure and the port of loading. This will be specifically stipulated in the contract agreement between the two parties.
Although in CIF terms, the seller must buy and bear insurance costs until the goods arrive at the destination port. However, this is just a form of the seller buying on behalf of the buyer. After completing the procedure, the seller will send all papers and documents. If there is a problem with the goods, the buyer will have the right to claim insurance, not the seller.
Once the commercial contract and CIF conditions have been signed, both the buyer and the seller will have the following responsibilities:
3.1 Regarding goods supply issues.
The seller will be responsible for checking, delivering goods, booking ships, and providing important documents to the buyer. On the contrary, the buyer will be responsible for paying the entire order value according to the contract signed by both parties.
3.2 Licenses and import-export procedures.
The seller is responsible for providing authorization documents, carrying out customs clearance procedures and export licenses. On the other side, the buyer needs to carry out procedures to apply for permission to import goods so that when the goods are transported to the port, the seller does not encounter obstacles from customs.
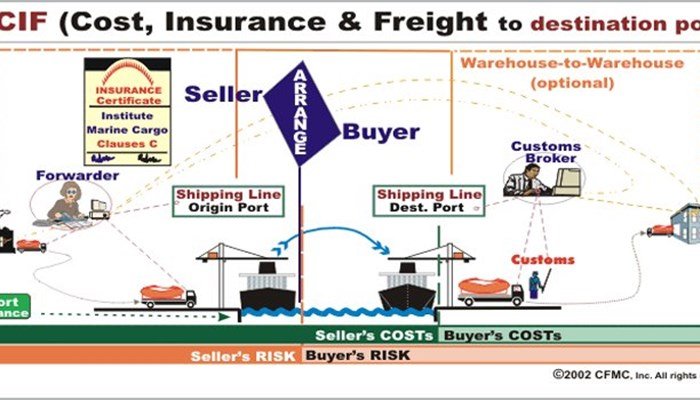
3.3 Shipping contract and order insurance fee.
The seller will proceed with the purchase and sign an insurance contract for the order. In addition, we pay all costs for shipping the shipment to the buyer's designated locations. The buyer is not required to sign transportation contracts or insurance contracts for the shipment.
3.4 Responsibilities for delivery and receipt of goods
The seller's primary responsibility is to transport and deliver the goods at the buyer's requested port. And the buyer will receive the goods at the previously designated port.
3.5 Transfer of risk in CIF
Although the seller will bear shipping fees as well as insurance fees. However, the risk transfer point is still at the ship's rail. When the seller has delivered the goods to the ship's deck, it means that the risk has been transferred from the seller to the buyer.
3.6 Total charges
In terms of costs, the seller will pay all expenses such as: shipping costs, loading and unloading of goods on board, customs declaration fees, export taxes, insurance fees, sea transportation fees... At that time, the buyer needs to pay the fees incurred when the goods are delivered to the ship by the buyer, import taxes, import customs procedures...
3.7 Proof of delivery and related information.
After the goods have been delivered on board, the seller will be responsible for delivering the original documents and papers related to the order to the buyer. The buyer will receive it in the most suitable form.
3.8 Row Check
The seller needs to pay all costs for product inspection, product quality management or packaging, and the buyer needs to pay related costs. quarantine in your country.
When to use FOB terms, when to use FOB terms CIF?
4.1 When should businesses use CIF terms
CIF terms will be suitable for loose goods, liquid goods or bulky goods. Companies that do not have much experience importing goods for the first time, or purchasing small volumes, should prioritize choosing CIF instead of other conditions
With CIF, your business will not need to waste time finding, booking shipping vessels and purchasing cargo insurance. The seller will be responsible for these things.
However, in reality, importing goods under CIF will cost more than FOB. The reason is that the buyer must pay an additional service fee for the seller to find a ship, buy insurance, pay shipping fees...
And because the buyer is not the one who directly charters the ship or uses the shipping service, it will be difficult for the buyer to control the quantity of goods as well as problems that arise during the delivery process. goods.
Compared with having to struggle to find shipping and insurance companies yourself, which takes more time... At this time, choosing CIF will be the most correct and suitable.
See more about conditions FOB
4.2 When should businesses use FOB terms?
FOB terms will be more suitable for businesses with extensive experience in the field import-export or businesses involved in large-scale import.
With this form, businesses will have to find and book ships themselves, so they can completely control freight and shipping costs. This also helps businesses save a significant amount of costs.
The cost of FOB is cheaper than CIF. And moreover, your business is also the person who rents and uses the services of the delivery party. Therefore, you can grasp all information about orders and promptly handle problems that arise.
The above is basic information about the content of CIF terms in Incoterms. Understanding CIF will help your business choose the most suitable purchasing and delivery method. Please contact Wingo Logistics when your business needs to import and export as well as transport international goods.


